What Is BODMAS Rule? | Solved Examples
What Is BODMAS Rule is a mathematical principle that defines the correct order of operations: Brackets, Orders (exponents), Division, Multiplication, Addition, and Subtraction for accurate calculations.
The BODMAS rule is a fundamental principle in mathematics that dictates the correct sequence of operations when solving an expression or equation.
BODMAS stands for Brackets, Orders (exponents and powers), Division, Multiplication, Addition, and Subtraction. The rule ensures that mathematical operations are performed in the right order to avoid confusion and errors.
According to BODMAS, operations inside brackets are solved first, followed by orders such as exponents. Next, division and multiplication are performed from left to right, followed by addition and subtraction, also from left to right. Understanding and applying the BODMAS rule is crucial for solving complex mathematical problems accurately and efficiently.
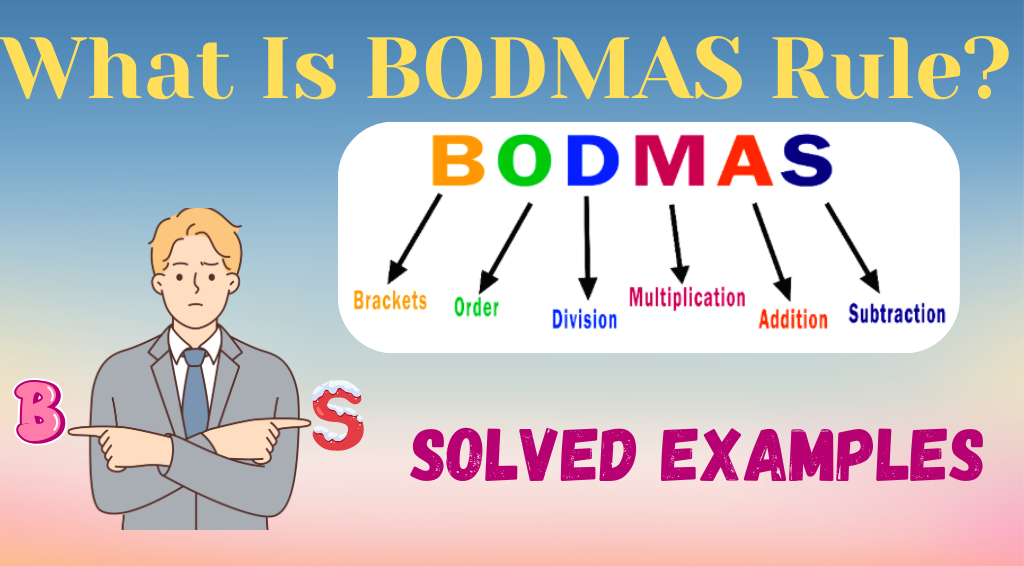
What is BODMAS?
BODMAS is an acronym that stands for Brackets, Orders, Division and Multiplication, Addition and Subtraction. It is a mathematical rule used to determine the correct order of operations when solving expressions.
According to BODMAS, operations inside brackets should be solved first. After that, any exponents or orders (such as squares, cubes, etc.) are dealt with.
Next, division and multiplication are performed from left to right, followed by addition and subtraction, also from left to right. This rule ensures that mathematical expressions are simplified correctly and consistently. By following BODMAS, you avoid confusion and achieve the correct result in calculations involving multiple operations.
What Is BODMAS
What is BODMAS Rule
Mathematics is a logic-based discipline that plays a crucial role in various aspects of our daily lives. In arithmetic, both numbers and operators are integral components of equations and expressions. Let’s break down these components further:
Numbers
Numbers represent mathematical values that signify a specific quantity and are used in counting and performing calculations. These values are often represented by symbols known as numerals, such as 3, 4, 8, and so on. Numbers can be categorized into different types, each serving distinct purposes in mathematics:
- Natural Numbers: The set of positive integers, starting from 1 (1, 2, 3, 4, …).
- Whole Numbers: Similar to natural numbers but include 0 (0, 1, 2, 3, …).
- Integers: Whole numbers and their negative counterparts (-3, -2, -1, 0, 1, 2, 3, …).
- Rational Numbers: Numbers that can be expressed as fractions or ratios (1/2, 3/4, 0.5, etc.).
- Irrational Numbers: Numbers that cannot be expressed as fractions and have non-repeating, non-terminating decimal expansions (√2, π).
- Real Numbers: The set of all rational and irrational numbers, representing any value on the number line.
- Complex Numbers: Numbers that include both real and imaginary components, often represented as a + bi (where “i” is the imaginary unit).
What Is BODMAS
Operators or Operations
Operators are symbols that denote mathematical operations applied to numbers, resulting in expressions or equations. The most commonly used operators in mathematics include:
- Addition (+): Combining two numbers to get their total.
- Subtraction (-): Finding the difference between two numbers.
- Multiplication (×): Combining numbers through repeated addition.
- Division (÷): Splitting one number by another to determine how many times the divisor fits into the dividend.
Order of Operations in BODMAS Rule
The BODMAS rule is a fundamental concept in mathematics that defines the order in which operations should be performed in expressions and equations. The acronym stands for:
- Brackets: First, solve expressions inside brackets (parentheses).
- Orders: Next, handle orders (exponents or powers).
- Division: Perform division from left to right.
- Multiplication: Perform multiplication from left to right.
- Addition: Perform addition from left to right.
- Subtraction: Finally, perform subtraction from left to right.
What Is BODMAS
Brackets are used to group terms together, ensuring that operations within them are performed first. This helps treat the grouped characters as a single entity, allowing the expression to be simplified correctly. Following the BODMAS rule ensures consistency and accuracy when solving mathematical problems, particularly those involving multiple operations.
In essence, the combination of numbers and operators, when handled with the appropriate order of operations, leads to the accurate resolution of complex mathematical expressions. Understanding and applying these fundamental principles is crucial for anyone working with mathematics, from basic arithmetic to advanced calculations.
Expression or an Equation of BODMAS
Here are examples of both an expression and an equation that illustrate the BODMAS rule:
Example of an Expression
Expression: ( 8 + 2 \times (3^2 – 1) \div 2 )
Step-by-Step Solution Using BODMAS:
- Brackets: Solve inside the brackets first.
- ( 3^2 – 1 = 9 – 1 = 8 )
- The expression now becomes: ( 8 + 2 \times 8 \div 2 )
- Orders: There are no further orders to solve.
- Division and Multiplication: From left to right.
- First, perform the multiplication: ( 2 \times 8 = 16 )
- Then, perform the division: ( 16 \div 2 = 8 )
- The expression now becomes: ( 8 + 8 )
- Addition: Finally, perform the addition.
- ( 8 + 8 = 16 )
Final Result: ( 16 )
What Is BODMAS
Example of an Equation
Equation: ( 4x + 3 = 19 )
Step-by-Step Solution:
- Isolate the variable: Start by subtracting 3 from both sides.
- ( 4x = 19 – 3 )
- ( 4x = 16 )
- Division: Divide both sides by 4 to solve for ( x ).
- ( x = \frac{16}{4} )
- ( x = 4 )
Final Result: ( x = 4 )
What Is BODMAS
Easy Ways to Remember the BODMAS Rule
Remembering the What Is BODMAS rule can be tricky, but there are some easy ways to recall it. Here are a few tips to help you remember the order of operations:
- A Simple Mnemonic: Use the phrase “BODMAS” itself or create a memorable sentence:
- Brackets
- Orders (Exponents)
- Division
- Multiplication
- Addition
- Subtraction
- Example: “Big Old Dogs Make Amazing Sounds.”
This simple phrase helps you recall the order of operations. - Visualize the Process: Imagine the BODMAS steps as a series of “layers,” starting with brackets as the innermost layer that gets solved first, then orders, followed by multiplication/division, and finally, addition/subtraction.
- Use Acronyms or Rhymes: Create an acronym that’s easy to remember. For example, “Please Excuse My Dear Aunt Sally” is a popular mnemonic for PEMDAS, the same rule used in the US (Parentheses, Exponents, Multiplication, Division, Addition, Subtraction).
- Practice with Examples: The more you practice solving problems following the BODMAS rule, the easier it will become to recall the order naturally. Regular practice helps reinforce the concept.
- Focus on the Importance of Order: The BODMAS rule is all about maintaining the right sequence. By focusing on the priority of operations (brackets first, then orders, followed by division/multiplication, and lastly addition/subtraction), you’ll get a sense of how to approach problems methodically.
What Is BODMAS
BODMAS and PEMDAS
BODMAS and PEMDAS are both acronyms used to remember the order of operations in mathematics. They serve the same purpose, but the terminology and regional preferences may differ. Here’s a breakdown of each rule:
BODMAS
BODMAS stands for:
- Brackets
- Orders (Exponents or Powers)
- Division
- Multiplication
- Addition
- Subtraction
What Is BODMAS
This rule indicates the sequence in which operations should be performed in an expression. It starts with operations inside brackets, followed by orders (exponents or powers like squares and square roots), then division and multiplication (from left to right), and finally addition and subtraction (from left to right).
PEMDAS
PEMDAS stands for:
- Parentheses
- Exponents
- Multiplication
- Division
- Addition
- Subtraction
PEMDAS is essentially the same as BODMAS, with “parentheses” used instead of “brackets” and “exponents” instead of “orders.” The rest of the operations follow in the same order. Just like BODMAS, multiplication and division are performed from left to right, as are addition and subtraction.
Key Differences Between BODMAS and PEMDAS:
- BODMAS is commonly used in the UK and other parts of the world.
- PEMDAS is more commonly used in the United States.
- Brackets in BODMAS are the same as Parentheses in PEMDAS.
- Orders in BODMAS refers to Exponents in PEMDAS.
What Is BODMAS
How Both Rules Work:
Both BODMAS and PEMDAS ensure that mathematical expressions are evaluated consistently and in the correct order.
For example, in the expression 3+4×23 + 4 \times 23+4×2, both rules dictate that multiplication should be done before addition, so the correct result is 3+8=113 + 8 = 113+8=11, not (3+4)×2=14(3 + 4) \times 2 = 14(3+4)×2=14.
What Is BODMAS
Read Also – Trigonometric Identities and Formula: Check Complete List
My name is Khushi, I am a content writer and I provide news related to government jobs and I am from Rajasthan and I only write on this website.
