What is Value of Pi in Maths: Definition, How To Calculate, Examples
What is Value of Pi is a mathematical constant representing the ratio of a circle’s circumference to its diameter. Discover its significance, formula, and historical background in this guide.
The Value of Pi (π) is one of the most important constants in mathematics, representing the ratio of a circle’s circumference to its diameter. It is an irrational number, meaning its decimal representation goes on infinitely without repeating.
The approximate value of Pi is 3.14159, but it can be calculated to billions of digits with the help of computers. Pi is essential in geometry, particularly in formulas related to circles and spheres, such as calculating the area of a circle (πr²) or the volume of a sphere (4/3πr³). Checkout the article to know more about the value of pi.
What is Value of Pi?
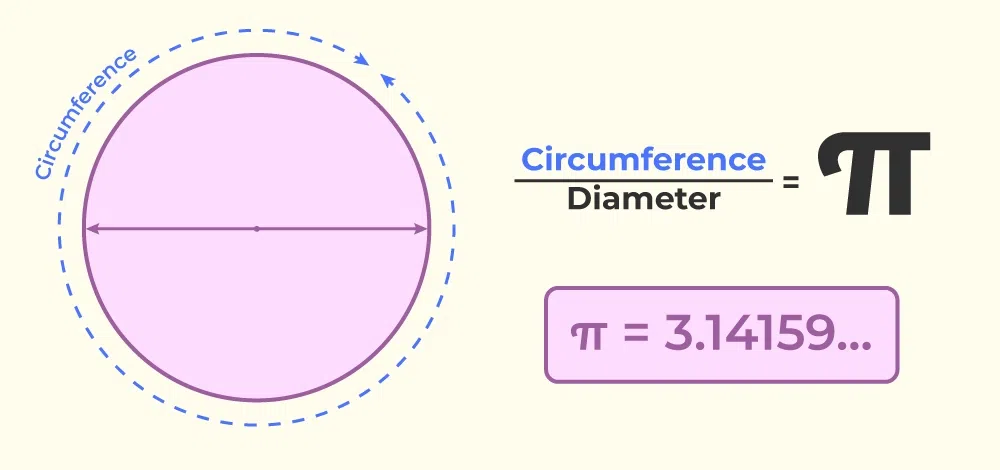
The value of ‘pi’ (π) is constant, meaning it remains unchanged. It is an irrational number typically approximated as 3.14. Pi is utilized in various formulas to calculate the surface area and volume of different solid shapes. Specifically, π is the ratio of a circle’s circumference to its diameter. The diameter of a circle is the longest line segment that passes through its centre.
Suppose we imagine bending the diameter line to cover a portion of the circle’s circumference. In that case, π represents the number of times the diameter can wrap around the circumference, approximately 3.14 times.
When we divide the circumference by the diameter, we consistently obtain a value close to 3.14. Importantly, regardless of the size of the circle drawn, the ratio of its circumference to its diameter will always remain the same.
Symbol for Pi
The symbol for Pi is π. This Greek letter has been adopted in mathematics to represent the ratio of a circle’s circumference to its diameter. The use of the symbol π was popularized by the Welsh mathematician William Jones in 1706, and it was later adopted by the Swiss mathematician Leonhard Euler in the 18th century.
The symbol π is now universally recognized in mathematics and is used in various formulas and equations related to geometry, trigonometry, and calculus. Its significance extends beyond mathematics into fields such as physics, engineering, and statistics, where it plays a crucial role in calculations involving circular and spherical shapes.
What is Value of Pi
Importance of Value of Pi
The value of Pi (π) plays a crucial role in mathematics and science, particularly in the fields of geometry, trigonometry, and physics. It is a fundamental constant that appears in various equations and formulas that help describe the world around us. Here are some reasons why the value of Pi is so significant:
-
Geometric Applications
Pi is fundamentally important in geometry, particularly when it comes to understanding circles. It represents the ratio of a circle’s circumference to its diameter, which is a constant value regardless of the circle’s size.
This relationship allows for the calculation of a circle’s circumference using the formula (C = 2\pi r), where ( r ) is the radius. Additionally, Pi is used to determine the area of a circle through the formula ( A = \pi r^2).
What is Value of Pi
-
Mathematical Significance
Pi is classified as an irrational number, meaning it cannot be expressed as a simple fraction, and its decimal representation is non-repeating and infinite. This property makes Pi a subject of fascination in number theory, as mathematicians have long sought to understand its properties and calculate its digits with ever-greater precision.
Furthermore, Pi is a transcendental number, which means it is not the root of any non-zero polynomial equation with rational coefficients. This characteristic has profound implications in various mathematical theories and highlights the complexity and richness of the number system.
What is Value of Pi
-
Statistics and Probability
In the field of statistics, Pi plays a vital role in the formulation of the normal distribution, a fundamental concept in probability theory. The normal distribution, often represented by the bell curve, describes how many natural phenomena are distributed and includes Pi in its mathematical equation.
Additionally, Pi appears in various mathematical models that explore randomness and chaos theory, making it relevant in fields such as cryptography and data analysis. Its presence in these areas underscores the interconnectedness of mathematics and real-world applications.
How to Calculate the Value of Pi?
Calculating the value of Pi (π) can be done using various methods, ranging from geometric approaches to infinite series and algorithms. Here are some of the most common methods used to approximate Pi:
1. Geometric Method (Archimedes’ Approach)
Archimedes was one of the first to calculate Pi using a geometric approach. He inscribed and circumscribed polygons around a circle and calculated their perimeters to estimate Pi.
What is Value of Pi
Steps:
- Start with a circle of radius (r).
- Inscribe a polygon (e.g., hexagon) inside the circle and calculate its perimeter.
- Circle a polygon around the circle and calculate its perimeter.
- As the number of sides of the polygons increases, the perimeters converge to the circumference of the circle, allowing for a better approximation of Pi.
2. Infinite Series
Several infinite series converge to Pi. One of the most famous is the Leibniz formula for Pi:
What is Value of Pi
Steps:
- Calculate the terms of the series until the desired precision is reached.
- Sum the terms and multiply by 4 to approximate Pi.
3. Monte Carlo Method
This probabilistic method uses random sampling to estimate Pi.
Steps:
- Draw a square with a circle inscribed within it.
- Randomly generate points within the square.
- Count how many points fall inside the circle versus the total number of points.
What is Value of Pi
Pi Values in Decimal
The value of Pi (π) is an irrational number, meaning it cannot be expressed exactly as a simple fraction and its decimal representation goes on infinitely without repeating. However, the first few decimal places of Pi are commonly used in mathematics and various fields of science and engineering. Here are the Pi values in decimal:
Pi Values in Decimal:
- π ≈ 3.14159
- π ≈ 3.1415926535
- π ≈ 3.141592653589793
- π ≈ 3.14159265358979323846
Although Pi continues indefinitely, the first 6 decimal places (3.141592) are often sufficient for most practical applications. In scientific work, more decimal places may be used for increased precision, especially in fields such as engineering, physics, and computer science.
What is Value of Pi
Relationship Between Diameter, Circumference, and the Value of Pi
The relationship between the diameter and circumference of a circle is fundamental in understanding the value of Pi (π). By dividing the circumference of a circle by its diameter, we obtain an approximation of Pi, which remains constant for all circles.
This ratio is approximately 3.14, but when calculated precisely, it continues infinitely without repeating. The following table illustrates how this relationship holds for various circle diameters, showcasing that the value of Pi is consistent across different circle sizes.
What is Value of Pi
| Diameter (units) | Circumference (units) | Circumference / Diameter |
| 1 | 3.1 | 3.1 / 1 = 3.1 |
| 2 | 6.2 (approx.) | 6.2 / 2 = 3.1 |
| 3 | 9.3 (approx.) | 9.3 / 3 = 3.1 |
| 4 | 12.4 (approx.) | 12.4 / 4 = 3.1 |
| 5 | 15.5 (approx.) | 15.5 / 5 = 3.1 |
Examples Using the Pi Value
Question:
A cyclist rides around a circular track with a diameter of 50 meters. How far has the cyclist ridden?
Solution:
To calculate the distance, we need to find the circumference of the circle.
Using the formula for circumference:
What is Value of Pi
Circumference=𝜋×Diameter
Here, the diameter of the track is 50 meters.
Circumference=3.14159×50 =157.0795 meters
What is Value of Pi
Read More – What Is BODMAS Rule? | Solved Examples
My name is Khushi, I am a content writer and I provide news related to government jobs and I am from Rajasthan and I only write on this website.